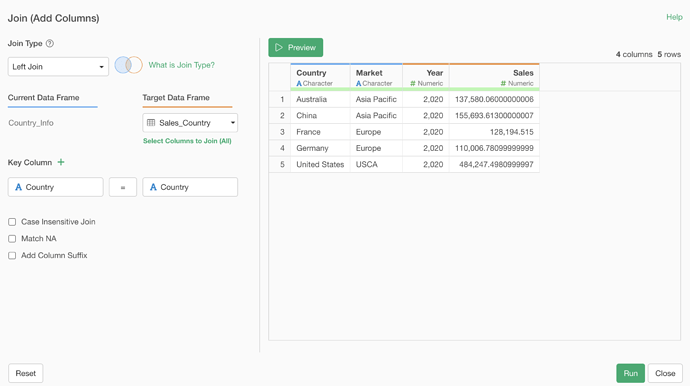
When the number of rows increases after a join, the likely cause is that there are duplicate rows for the values specified as the key column in the target data.
For example, suppose you have the following data.
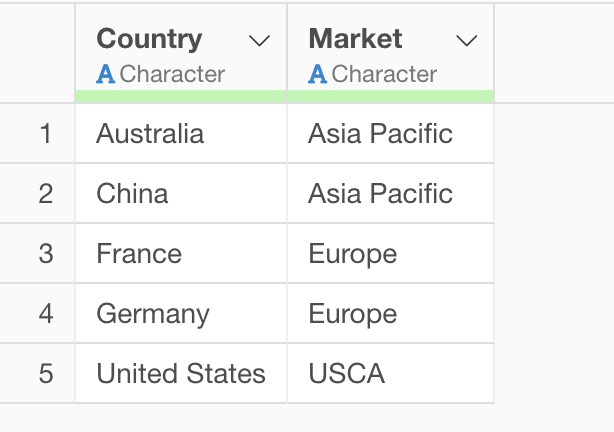
Country Information Data
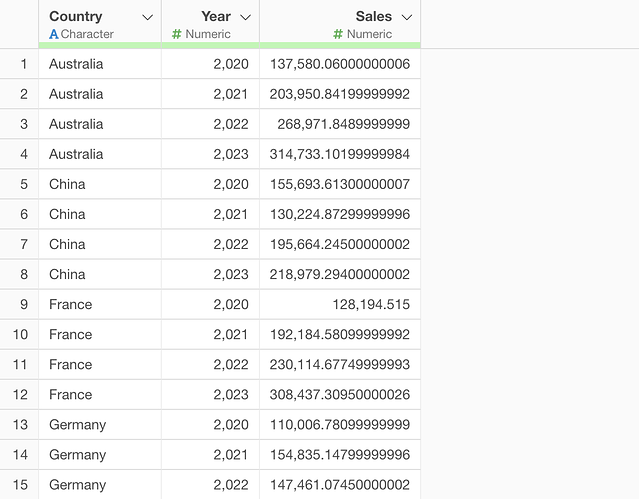
Yearly Sales Data
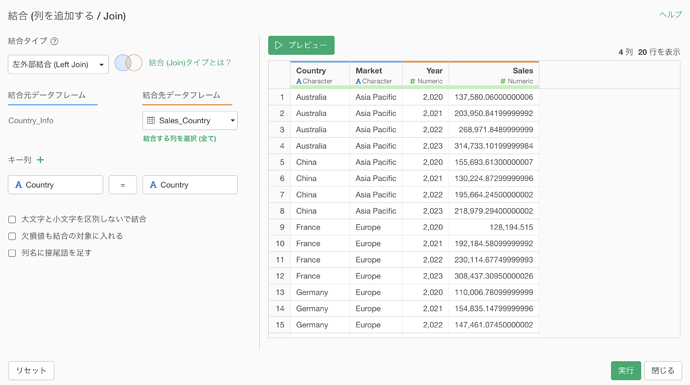
When you join to the Country Information data using the Country column as the key, you can see that each country has increased by 4 rows because the target data contains 4 years of data, as shown below.
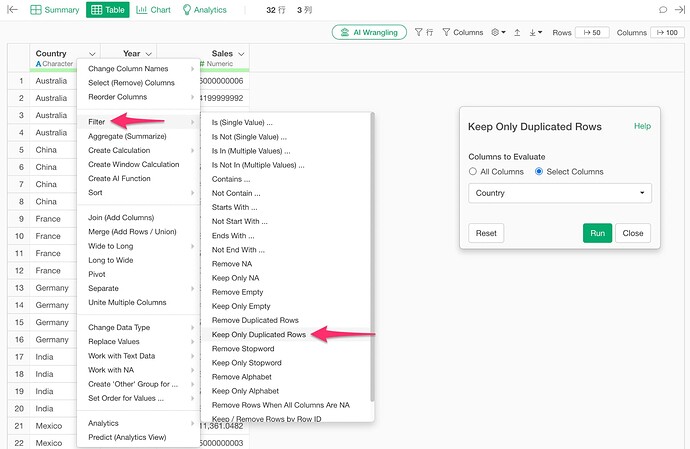
If you want to find out which values in the key column are duplicated in the target data, you can use “Keep Only Duplicate Rows” in the Filter to investigate.
If you have specified multiple key columns for the join, select all the columns specified as key columns when keeping only duplicate rows.
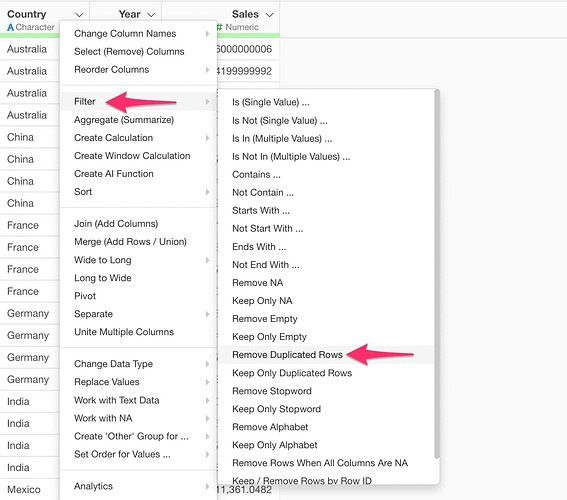
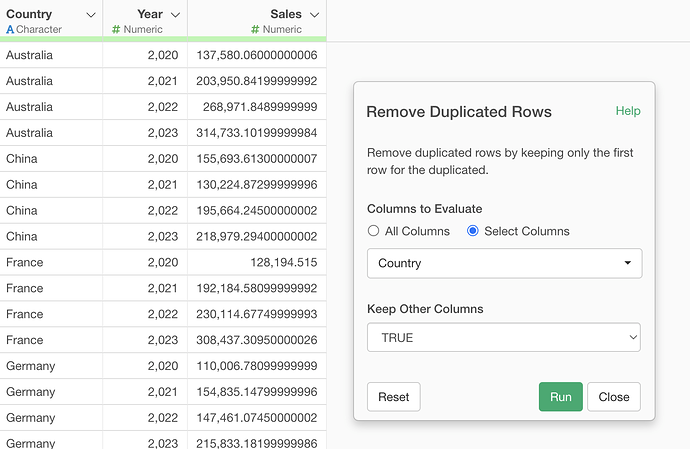
If you want to remove duplicate rows from the target data, select “Remove Duplicate Rows” from the “Filter” on the column used as the join key in the target data.
The Remove Duplicate Rows dialog will appear, so go ahead and run it.
This removes the duplicate rows from the target data, so the number of rows will no longer increase when joining.